
This is the fifth installment of our masterclass series. In this part, we transition from financial structures into Operations and Inventory Management. We will build a robust Product Management system, covering everything from database schema to a modern UI that handles product images and duplicate SKU verification including Store Management.
Explanation with timeline
Module Overview: Introduction to the inventory module and its importance in calculating the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS).
The Product Table Architecture: Defining the tbl_Items with fields for Name, Type, Detail, Factor, Units, Opening Stock, Total Stock, Warning units, re-order units, sale price, and store ID.
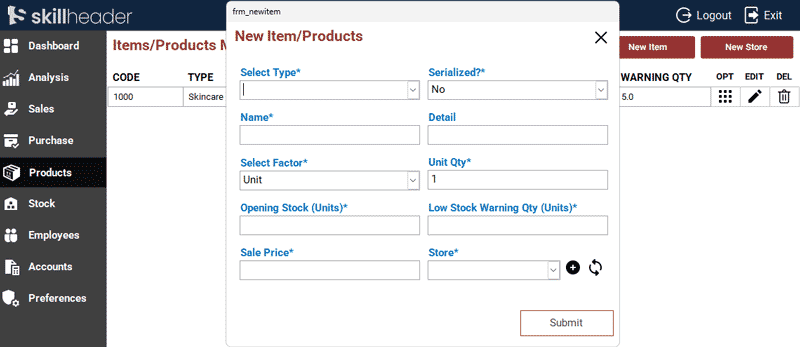
Designing the Product Entry Form: Creating a professional interface to add Items and Products based on the table fields.
Dynamic Type/Category Selection: Implementing a Combo Box to select category or Type of the Item.
The Submit Logic: Writing the VBA code to handle both new entries and record updates, followed by our modern pop-up alert. contact@skillheader.com
The Store Table and Form Building: Second table tbl_store with the fields of store ID, date, name, location, address, person, phone, audit interval days, audit reminder, employee ID, and audit start date.
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide
In this session, we establish the foundation of the inventory system. Proper items and product setup is vital for accurate sales tracking and automated stock reordering.
1. Database Architecture: Tables
To keep the system normalized, we create Items or Products and store tables:
1.1. The Product Table (Products_tbl) This table stores all the static and dynamic data for your items.
| Field Name | Data Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
ItmID | AutoNumber (Primary Key) | Unique ID for the Item entry. |
ItmCode | Number | Item Code to integrate with other tables. |
ItmSerialized | Text | Yes/No condition to determine auto serial with items or not (This is helpful to generate tags) |
ItmNm | Text | Item or Product name |
ItmType | Text | Type or Category of the item |
ItmDetail | Text | Short description about the item |
ItmFactor | Text | Item Packaging type (e.g., Unit, Box) |
ItmUnits | Number | Number of Units in a factor/pack |
ItmOStock | Number | Opening Stock |
ItmOTotal | Number | Number of Opening Stock Units |
ItmWarningUnits | Number | Low Stock Warning Quantity in Number of Units |
ItmReOrderUnits | Number | Reorder Quantity in Number Units |
ItmSalePrice | Currency | Sale Price |
ItmStoreID | Number | Linked Store ID |
1.2 The Store Table (tbl_Store): To define physical locations like “Main Warehouse,” “Shop Floor,” or “Cold Storage.”
| Field Name | Data Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
StoreID | AutoNumber (Primary Key) | Unique ID for the Store entry. |
StoreDt | Date/Time | Store registration date |
StoreNm | Text | Store Name |
StoreLocation | Text | Store Location (Internal or External) |
StoreAddress | Text | Store Physical Address |
StorePerson | Text | Store Keeper Name |
StorePhone | Text | Store Keeper Contact Number |
StoreAuditIntervalDays | Number | Store Audit Interval Days |
StoreReminder | Text | Yes/No to set the reminder for Audit |
StoreEmpID | Number | Employee ID in case of Store Keeper is an Employee |
StoreAuditStartDt | Date/Time | Beginning date of the Audit |
2. Building the ‘Add New Items’ Form (frm_NewItem)
frm_NewItem)2.1. Form Interface (frm_NewItem)
frm_NewItem)- Unbound Form: The form is converted to an Unbound Form
(frm_NewItem)for strict control over data before insertion. - Data Entry: Create textboxes for Item Name, Detail, Factor, Units, Stock, Level, and Price.
- Item Categories: A combo box with manual Value List items for the type or categories.
- Use a Combo Box to display all store accounts.

2.2. Submit Button VBA Logic and Code
- Checks for empty mandatory fields.
- Generates Item Code with the addition of 1.
- Enters data into the Items Table
(tbl_Items). - Triggers the confirmation popup message.
Private Sub Cmd_SubmitNewItem_Click()
If IsNull(Me.txt_ItmType) = True Or IsNull(Me.txt_ItmSerialized) = True Or IsNull(Me.txt_ItmNm) = True Or _
IsNull(Me.txt_ItmFactor) = True Or IsNull(Me.txt_ItmUnits) = True Or IsNull(Me.txt_ItmOStock) = True Or _
IsNull(Me.txt_ItmWarningUnits) = True Or IsNull(Me.txt_ItmSalePrice) = True Or IsNull(Me.txt_ItmStoreID) = True Then
MsgBox "Mandator fields must be filled !", , "|Empty Textboxes|"
Exit Sub
Else
'Generating Item Code
dc = DCount("*", "tbl_Items")
If dc > 0 Then
dcc = DLast("ItmCode", "tbl_Items") + 1
Else
'If table has no data
dcc = 1000
End If
Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset("tbl_Items", dbOpenDynaset, dbsechanges)
With rst
.AddNew
.Fields("ItmType") = Me.txt_ItmType
.Fields("ItmCode") = dcc
.Fields("ItmSerialized") = Me.txt_ItmSerialized
.Fields("ItmNm") = Me.txt_ItmNm
.Fields("ItmDetail") = Me.txt_ItmDetail
.Fields("ItmFactor") = Me.txt_ItmFactor
.Fields("ItmUnits") = Me.txt_ItmUnits
.Fields("ItmOStock") = Me.txt_ItmOStock
.Fields("ItmOTotal") = Me.txt_ItmOStock
.Fields("ItmWarningUnits") = Me.txt_ItmWarningUnits
.Fields("ItmSalePrice") = Me.txt_ItmSalePrice
.Fields("ItmStoreID") = Me.txt_ItmStoreID.Column(0)
.Update
End With
Set rst = Nothing
DoCmd.Close acForm, "frm_NewItem"
'\\\MsgPopup
DoCmd.OpenForm "frm_msgpopup"
Forms!frm_msgpopup.Form.LblMsgPopup.Caption = "New Item has been added.."
'Refresh the data in the Main form
Forms!MainDashboard!NavigationSubform.Form.Requery
End If
End Sub3. Building the ‘Add New Store’ Form (frm_NewStore)
frm_NewStore)3.1. Form Interface (frm_NewStore)
frm_NewStore)- Unbound Form: The form is converted to an Unbound Form
(frm_NewStore)for strict control over data before insertion. - Data Entry: Create textboxes for Store Name, Location, Address, Contact Person, Phone, and Audit Interval Days.
3.2. Submit Button VBA Logic and Code for (frm_NewStore)
- Checks for empty mandatory fields.
- Enters data into the Store Table
(tbl_Stores). - Triggers the confirmation popup message.
Private Sub Cmd_SubmitNewStore_Click()
If IsNull(Me.txt_StoreDt) = True Or IsNull(Me.txt_StoreNm) = True Or IsNull(Me.txt_StoreLocation) = True Or _
IsNull(Me.txt_StoreAddress) = True Or IsNull(Me.txt_StorePerson) = True Or IsNull(Me.txt_StorePhone) = True Or _
IsNull(Me.txt_StoreAuditIntervalDays) = True Then
MsgBox "Mandator fields must be filled !", , "|Empty Textboxes|"
Exit Sub
Else
Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset("tbl_Store", dbOpenDynaset, dbsechanges)
With rst
.AddNew
.Fields("StoreDt") = Me.txt_StoreDt
.Fields("StoreNm") = Me.txt_StoreNm
.Fields("StoreLocation") = Me.txt_StoreLocation
.Fields("StoreAddress") = Me.txt_StoreAddress
.Fields("StorePerson") = Me.txt_StorePerson
.Fields("StorePhone") = Me.txt_StorePhone
.Fields("StoreAuditIntervalDays") = Me.txt_StoreAuditIntervalDays
.Update
End With
Set rst = Nothing
DoCmd.Close acForm, "frm_NewStore"
'\\\MsgPopup
DoCmd.OpenForm "frm_msgpopup"
Forms!frm_msgpopup.Form.LblMsgPopup.Caption = "New Store has been Created.."
'Refresh the data in the Main form
Forms!MainDashboard!NavigationSubform.Form.Requery
End If
End Sub


